The Musculocutaneous, Axillary, & Spinal Accessory Nerves
...
The Musculocutaneous
This nerve can be studied when lesions involve the nerve itself, a C5 or C6 root or the upper trunk or lateral cord of the brachial plexus. In routine nerve conduction, however, it is mainly used in repetitive stimulation.
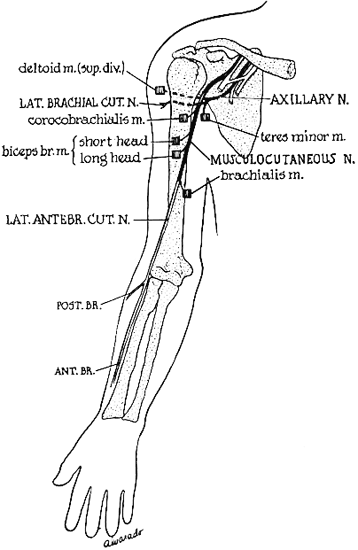
The motor fibers can be stimulated at the axilla and supraclavicular fossa and the motor response recorded from the belly of the biceps. Use a small ground electrode for active electrode because of the size of the muscle. Place the reference electrode over the elbow and the ground between the active electrode and the axilla.
The sensory fibers (the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve) can be stimulated at the elbow, just lateral to the biceps tendon and the sensory response recorded 12 cm distal to the cathode over the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Musculocutaneous Entrapment, Compression Or Injury Sites
The musculocutaneous nerve is seldom involved by injury alone. When it is, trauma is the cause and can occur at any point along the nerve.
Axillary Nerve
This nerve is studied when lesions involve the nerve itself, a C5 root, or the posterior cord or upper trunk of the brachial plexus. Its most coomon use, however, is in performing repetitive stimulation.
Record the motor response from the deltoid by means of a small ground electrode as the active electrode. Place the reference over the elbow and the ground between the active electrode and the stimulator. This nerve can be stimulated in the supraclavicular fossa.
Axillary Entrapment, Compression Or Injury Sites
The axillary nerve is especially vulnerable to injury as it winds around the lateral aspect of the humerus where it can be involved either by fractures of the humerus or shoulder dislocation.
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Stimulate the nerve in the neck halfway between the mastoid process and the clavicle behind the belly of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Record the motor response from the belly of the upper trapezius, easily located by asking the subject to shrug their shoulders. Use a ground electrode as the active electrode and place the reference over the shoulder. Place the ground between the active and stimulating electrodes. This nerve is most commonly used for repetitive stimulation.
Spinal Accessory Entrapment, Compression Or Injury Sites
The spinal accessory nerve is most susceptible to injury in its superficial course through the posterior cervical triangle (causing trapezius palsy) and less frequently above the sternomastoid branch (with resulting trapezius and sternomastoid weakness).
